Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible
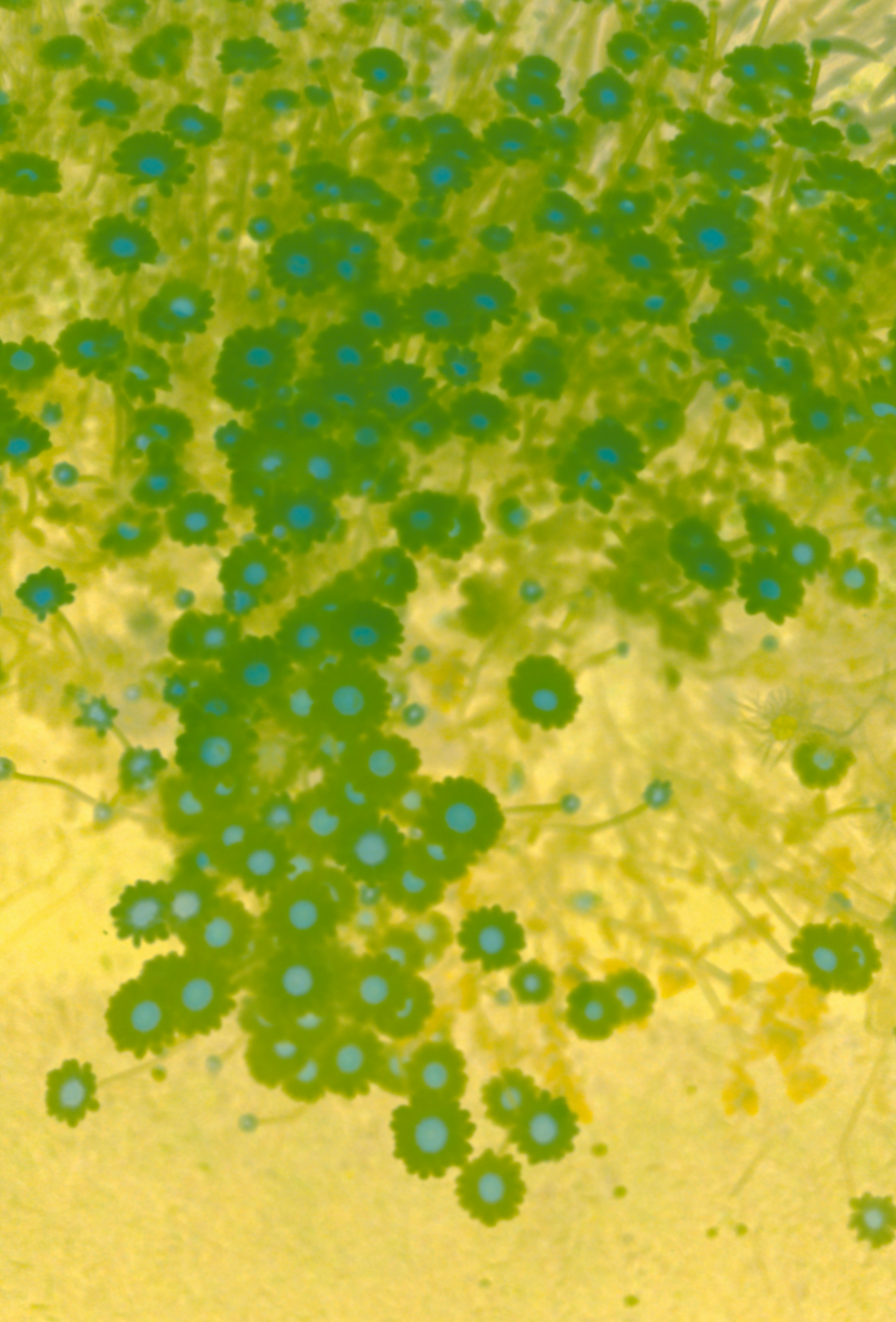
Your guide to Peripheral Blood Film.
Understand the importance of Peripheral Blood Film in assessing your health with Mito Health's comprehensive biomarker analysis. Our detailed reports, covering 67 key biomarkers, provide crucial insights to help you make informed decisions for a longer, healthier life.

Written by
Mito Health

What is Peripheral Blood Film?
A peripheral blood film is a laboratory technique used to examine blood cells under a microscope.A small drop of blood is spread onto a glass slide, stained with special dyes, and analyzed to assess the characteristics of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What does it assess?
This test helps diagnose and monitor various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, infections, and clotting issues.It provides essential information on the morphology (shape, size, and number) of the cells and is used in conjunction with other blood tests to evaluate a person's overall health.
How do I optimize my Peripheral Blood Film results?
The bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, so supporting bone marrow health is crucial.Practices such as regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding substances that can harm the bone marrow are key to optimizing blood production. Exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals or certain chemicals, can cause abnormalities in blood cell morphology.Limiting exposure to environmental toxins or harmful substances, like alcohol and smoking, can reduce the risk of blood cell abnormalities. Conditions such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, or infections can impact blood cell morphology.Regular medical check-ups to monitor these conditions and manage them appropriately will help maintain healthy peripheral blood film results.
What do good and bad Peripheral Blood Film results look like?
If a blood smear reveals an increased number of abnormal cells, it may suggest conditions such as leukemia, bone marrow disorders, or infections. The presence of immature white blood cells could indicate leukemia or another form of bone marrow failure.A decrease in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets on the smear may indicate a condition such as anemia, bone marrow suppression, or a failure in blood cell production. The presence of abnormally shaped red blood cells could suggest nutritional deficiencies, chronic disease, or inherited disorders affecting blood cells.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-peripheral-blood-film-naturally
Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible

Comments
Your guide to Peripheral Blood Film.
Understand the importance of Peripheral Blood Film in assessing your health with Mito Health's comprehensive biomarker analysis. Our detailed reports, covering 67 key biomarkers, provide crucial insights to help you make informed decisions for a longer, healthier life.

Written by
Mito Health

What is Peripheral Blood Film?
A peripheral blood film is a laboratory technique used to examine blood cells under a microscope.A small drop of blood is spread onto a glass slide, stained with special dyes, and analyzed to assess the characteristics of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What does it assess?
This test helps diagnose and monitor various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, infections, and clotting issues.It provides essential information on the morphology (shape, size, and number) of the cells and is used in conjunction with other blood tests to evaluate a person's overall health.
How do I optimize my Peripheral Blood Film results?
The bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, so supporting bone marrow health is crucial.Practices such as regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding substances that can harm the bone marrow are key to optimizing blood production. Exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals or certain chemicals, can cause abnormalities in blood cell morphology.Limiting exposure to environmental toxins or harmful substances, like alcohol and smoking, can reduce the risk of blood cell abnormalities. Conditions such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, or infections can impact blood cell morphology.Regular medical check-ups to monitor these conditions and manage them appropriately will help maintain healthy peripheral blood film results.
What do good and bad Peripheral Blood Film results look like?
If a blood smear reveals an increased number of abnormal cells, it may suggest conditions such as leukemia, bone marrow disorders, or infections. The presence of immature white blood cells could indicate leukemia or another form of bone marrow failure.A decrease in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets on the smear may indicate a condition such as anemia, bone marrow suppression, or a failure in blood cell production. The presence of abnormally shaped red blood cells could suggest nutritional deficiencies, chronic disease, or inherited disorders affecting blood cells.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-peripheral-blood-film-naturally
Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible

Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible
Comments
Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible
Your guide to Peripheral Blood Film.
Understand the importance of Peripheral Blood Film in assessing your health with Mito Health's comprehensive biomarker analysis. Our detailed reports, covering 67 key biomarkers, provide crucial insights to help you make informed decisions for a longer, healthier life.

Written by
Mito Health

What is Peripheral Blood Film?
A peripheral blood film is a laboratory technique used to examine blood cells under a microscope.A small drop of blood is spread onto a glass slide, stained with special dyes, and analyzed to assess the characteristics of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What does it assess?
This test helps diagnose and monitor various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, infections, and clotting issues.It provides essential information on the morphology (shape, size, and number) of the cells and is used in conjunction with other blood tests to evaluate a person's overall health.
How do I optimize my Peripheral Blood Film results?
The bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, so supporting bone marrow health is crucial.Practices such as regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding substances that can harm the bone marrow are key to optimizing blood production. Exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals or certain chemicals, can cause abnormalities in blood cell morphology.Limiting exposure to environmental toxins or harmful substances, like alcohol and smoking, can reduce the risk of blood cell abnormalities. Conditions such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, or infections can impact blood cell morphology.Regular medical check-ups to monitor these conditions and manage them appropriately will help maintain healthy peripheral blood film results.
What do good and bad Peripheral Blood Film results look like?
If a blood smear reveals an increased number of abnormal cells, it may suggest conditions such as leukemia, bone marrow disorders, or infections. The presence of immature white blood cells could indicate leukemia or another form of bone marrow failure.A decrease in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets on the smear may indicate a condition such as anemia, bone marrow suppression, or a failure in blood cell production. The presence of abnormally shaped red blood cells could suggest nutritional deficiencies, chronic disease, or inherited disorders affecting blood cells.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-peripheral-blood-film-naturally
Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible

Comments
Your guide to Peripheral Blood Film.
Understand the importance of Peripheral Blood Film in assessing your health with Mito Health's comprehensive biomarker analysis. Our detailed reports, covering 67 key biomarkers, provide crucial insights to help you make informed decisions for a longer, healthier life.

Written by
Mito Health

What is Peripheral Blood Film?
A peripheral blood film is a laboratory technique used to examine blood cells under a microscope.A small drop of blood is spread onto a glass slide, stained with special dyes, and analyzed to assess the characteristics of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What does it assess?
This test helps diagnose and monitor various blood disorders, such as anemia, leukemia, infections, and clotting issues.It provides essential information on the morphology (shape, size, and number) of the cells and is used in conjunction with other blood tests to evaluate a person's overall health.
How do I optimize my Peripheral Blood Film results?
The bone marrow is responsible for producing blood cells, so supporting bone marrow health is crucial.Practices such as regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding substances that can harm the bone marrow are key to optimizing blood production. Exposure to toxins, such as heavy metals or certain chemicals, can cause abnormalities in blood cell morphology.Limiting exposure to environmental toxins or harmful substances, like alcohol and smoking, can reduce the risk of blood cell abnormalities. Conditions such as chronic inflammation, autoimmune disorders, or infections can impact blood cell morphology.Regular medical check-ups to monitor these conditions and manage them appropriately will help maintain healthy peripheral blood film results.
What do good and bad Peripheral Blood Film results look like?
If a blood smear reveals an increased number of abnormal cells, it may suggest conditions such as leukemia, bone marrow disorders, or infections. The presence of immature white blood cells could indicate leukemia or another form of bone marrow failure.A decrease in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets on the smear may indicate a condition such as anemia, bone marrow suppression, or a failure in blood cell production. The presence of abnormally shaped red blood cells could suggest nutritional deficiencies, chronic disease, or inherited disorders affecting blood cells.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-peripheral-blood-film-naturally
Get a deeper look into your health.
Schedule online, results in a week
Clear guidance, follow-up care available
HSA/FSA Eligible

Comments
Recently published
What's included

1 Comprehensive lab test (Core)
One appointment, test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

Personalized health insights & action plan
In-depth recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Valentine's Offer: Get $75 off your membership
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$324
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle
(For 2)
$798
$563
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform
What's included

1 Comprehensive lab test (Core)
One appointment, test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

Personalized health insights & action plan
In-depth recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Valentine's Offer: Get $75 off your membership
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$324
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle (For 2)
$798
$563
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform
What's included

1 Comprehensive lab test (Core)
One appointment, test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

Personalized health insights & action plan
In-depth recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Valentine's Offer: Get $75 off your membership
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$324
/year
or 4 payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle
(For 2)
$798
$563
/year
or 4 payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform