Mito Health: Helping you live healthier, longer.
In-depth bloodwork & holistic health advice, backed by the latest longevity science. Only $399.
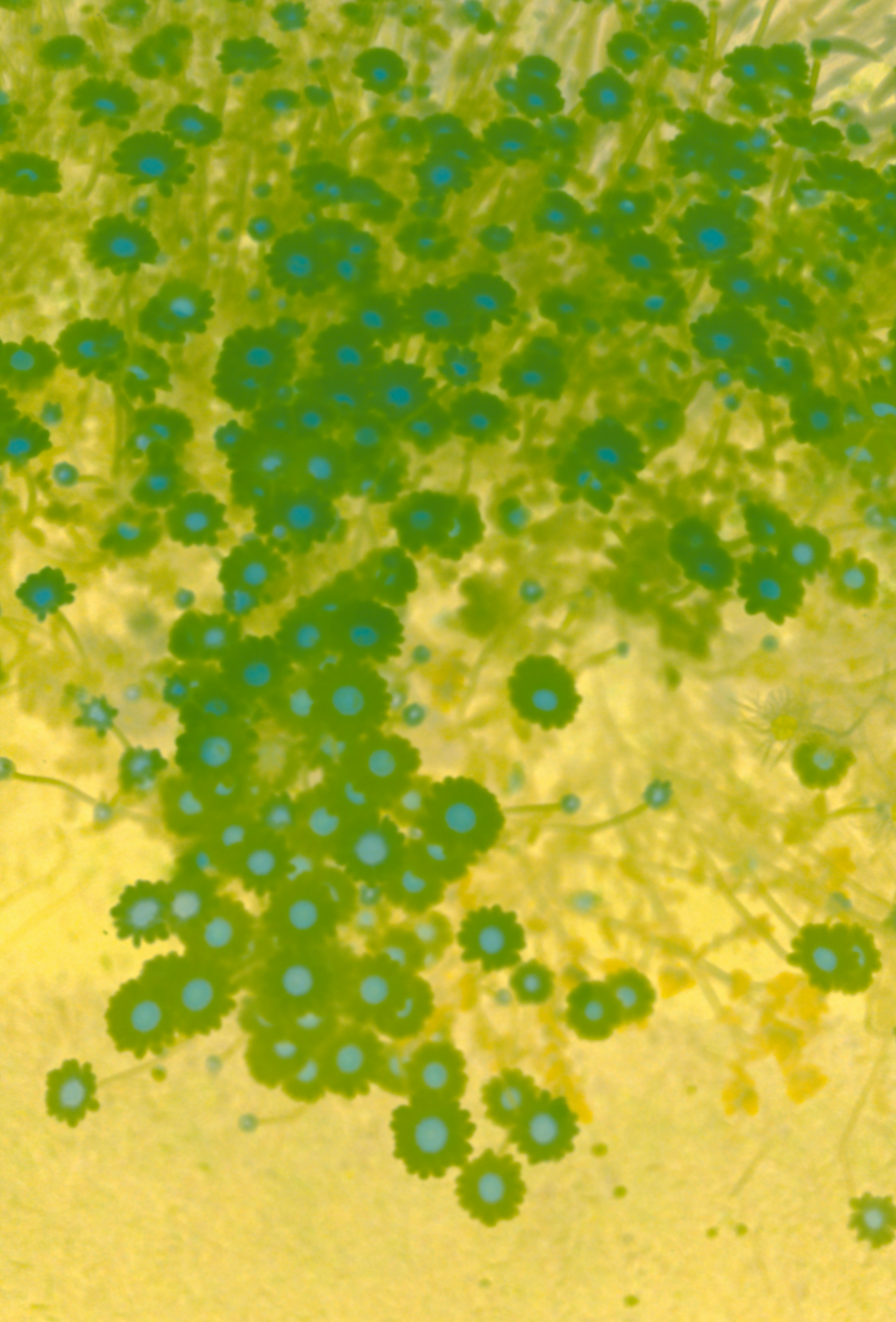
Neutrophils: Your Frontline Defense Cells
Neutrophils are first responders to infection. Abnormal counts can indicate infection, inflammation, or immune disorders.

Written by
Mito Team

What are Neutrophils?
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell, and they play a crucial role in your body's immune system.These cells are like your body's first responders, rushing to the site of infection or injury to combat pathogens such as bacteria and fungi.They engulf and digest these invaders through a process called phagocytosis.Measuring the level of neutrophils in your blood gives us valuable information about your immune system's current state and its ability to respond to threats.
What does it assess?
Neutrophil levels are directly related to your healthspan because they are integral to your body's defence mechanisms.A normal neutrophil count indicates a robust immune system capable of effectively fighting infections and responding to injuries.
How do I optimize my Neutrophil levels?
Eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and folate, can support the production and function of neutrophils.Foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, and lean proteins help maintain optimal immune function. Moderate physical activity can enhance immune function and help the body maintain a healthy neutrophil count.However, excessive intense exercise can suppress neutrophil production, so balance is key. Chronic stress can suppress immune function and affect neutrophil production.Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve immune health.
What do high and low Neutrophil levels mean?
An elevated neutrophil count, or neutrophilia, typically indicates an acute bacterial infection, such as pneumonia, appendicitis, or an abscess.It can also be caused by inflammatory conditions, tissue damage, stress responses, or certain medications like corticosteroids.A low neutrophil count, or neutropenia, can lead to a weakened immune system and increased vulnerability to infections.Causes of neutropenia include viral infections (e.g., HIV), bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and certain medications.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-high-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-low-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-naturally
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-percentage-naturally
Neutrophils: Your Frontline Defense Cells
Neutrophils are first responders to infection. Abnormal counts can indicate infection, inflammation, or immune disorders.

Written by
Mito Team

What are Neutrophils?
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell, and they play a crucial role in your body's immune system.These cells are like your body's first responders, rushing to the site of infection or injury to combat pathogens such as bacteria and fungi.They engulf and digest these invaders through a process called phagocytosis.Measuring the level of neutrophils in your blood gives us valuable information about your immune system's current state and its ability to respond to threats.
What does it assess?
Neutrophil levels are directly related to your healthspan because they are integral to your body's defence mechanisms.A normal neutrophil count indicates a robust immune system capable of effectively fighting infections and responding to injuries.
How do I optimize my Neutrophil levels?
Eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and folate, can support the production and function of neutrophils.Foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, and lean proteins help maintain optimal immune function. Moderate physical activity can enhance immune function and help the body maintain a healthy neutrophil count.However, excessive intense exercise can suppress neutrophil production, so balance is key. Chronic stress can suppress immune function and affect neutrophil production.Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve immune health.
What do high and low Neutrophil levels mean?
An elevated neutrophil count, or neutrophilia, typically indicates an acute bacterial infection, such as pneumonia, appendicitis, or an abscess.It can also be caused by inflammatory conditions, tissue damage, stress responses, or certain medications like corticosteroids.A low neutrophil count, or neutropenia, can lead to a weakened immune system and increased vulnerability to infections.Causes of neutropenia include viral infections (e.g., HIV), bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and certain medications.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-high-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-low-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-naturally
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-percentage-naturally
Mito Health: Helping you live healthier, longer.
In-depth bloodwork & holistic health advice, backed by the latest longevity science. Only $399.
Mito Health: Helping you live healthier, longer.
In-depth bloodwork & holistic health advice, backed by the latest longevity science. Only $399.
Neutrophils: Your Frontline Defense Cells
Neutrophils are first responders to infection. Abnormal counts can indicate infection, inflammation, or immune disorders.

Written by
Mito Team

What are Neutrophils?
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell, and they play a crucial role in your body's immune system.These cells are like your body's first responders, rushing to the site of infection or injury to combat pathogens such as bacteria and fungi.They engulf and digest these invaders through a process called phagocytosis.Measuring the level of neutrophils in your blood gives us valuable information about your immune system's current state and its ability to respond to threats.
What does it assess?
Neutrophil levels are directly related to your healthspan because they are integral to your body's defence mechanisms.A normal neutrophil count indicates a robust immune system capable of effectively fighting infections and responding to injuries.
How do I optimize my Neutrophil levels?
Eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and folate, can support the production and function of neutrophils.Foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, and lean proteins help maintain optimal immune function. Moderate physical activity can enhance immune function and help the body maintain a healthy neutrophil count.However, excessive intense exercise can suppress neutrophil production, so balance is key. Chronic stress can suppress immune function and affect neutrophil production.Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve immune health.
What do high and low Neutrophil levels mean?
An elevated neutrophil count, or neutrophilia, typically indicates an acute bacterial infection, such as pneumonia, appendicitis, or an abscess.It can also be caused by inflammatory conditions, tissue damage, stress responses, or certain medications like corticosteroids.A low neutrophil count, or neutropenia, can lead to a weakened immune system and increased vulnerability to infections.Causes of neutropenia include viral infections (e.g., HIV), bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and certain medications.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-high-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-low-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-naturally
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-percentage-naturally
Mito Health: Helping you live healthier, longer.
In-depth bloodwork & holistic health advice, backed by the latest longevity science. Only $399.
Neutrophils: Your Frontline Defense Cells
Neutrophils are first responders to infection. Abnormal counts can indicate infection, inflammation, or immune disorders.

Written by
Mito Team

What are Neutrophils?
Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell, and they play a crucial role in your body's immune system.These cells are like your body's first responders, rushing to the site of infection or injury to combat pathogens such as bacteria and fungi.They engulf and digest these invaders through a process called phagocytosis.Measuring the level of neutrophils in your blood gives us valuable information about your immune system's current state and its ability to respond to threats.
What does it assess?
Neutrophil levels are directly related to your healthspan because they are integral to your body's defence mechanisms.A normal neutrophil count indicates a robust immune system capable of effectively fighting infections and responding to injuries.
How do I optimize my Neutrophil levels?
Eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, vitamin E, zinc, and folate, can support the production and function of neutrophils.Foods like citrus fruits, leafy greens, and lean proteins help maintain optimal immune function. Moderate physical activity can enhance immune function and help the body maintain a healthy neutrophil count.However, excessive intense exercise can suppress neutrophil production, so balance is key. Chronic stress can suppress immune function and affect neutrophil production.Practicing stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and improve immune health.
What do high and low Neutrophil levels mean?
An elevated neutrophil count, or neutrophilia, typically indicates an acute bacterial infection, such as pneumonia, appendicitis, or an abscess.It can also be caused by inflammatory conditions, tissue damage, stress responses, or certain medications like corticosteroids.A low neutrophil count, or neutropenia, can lead to a weakened immune system and increased vulnerability to infections.Causes of neutropenia include viral infections (e.g., HIV), bone marrow disorders, autoimmune diseases, chemotherapy, and certain medications.
Related MitoHealth Reads
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-high-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/symptom-levels/symptoms-of-low-neutrophils
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-naturally
https://mitohealth.com/improve/how-to-improve-your-neutrophils-percentage-naturally
Recently published
What's included

Comprehensive lab testing (Core)
100+ biomarkers - Test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

In-depth health insights & action plan
Expert designed recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Exclusive offer. Save $50.
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$349
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle
(For 2)
$798
$668
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform
What's included

Comprehensive lab testing (Core)
100+ biomarkers - Test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

In-depth health insights & action plan
Expert designed recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Exclusive offer. Save $50.
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$349
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle (For 2)
$798
$668
/year
or 4 interest-free payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform
What's included

Comprehensive lab testing (Core)
100+ biomarkers - Test at 2,000+ labs nationwide

In-depth health insights & action plan
Expert designed recommendations across exercise, nutrition, and supplements

1:1 Consultation
Meet with your dedicated care team to review your results and define next steps

Lifetime health record tracking
Upload past labs and monitor your progress over time

Biological age analysis
See how your body is aging and what’s driving it

Order add-on tests and scans anytime
Access to advanced diagnostics at discounted rates for members
Concierge-level care, made accessible.
Exclusive offer. Save $50.
Codeveloped with experts at MIT & Stanford
Less than $1/ day
Billed annually - cancel anytime
Bundle options:
Individual
$399
$349
/year
or 4 payments of $87.25*
Duo Bundle
(For 2)
$798
$668
/year
or 4 payments of $167*
Pricing for members in NY, NJ & RI may vary.

Checkout with HSA/FSA
Secure, private platform